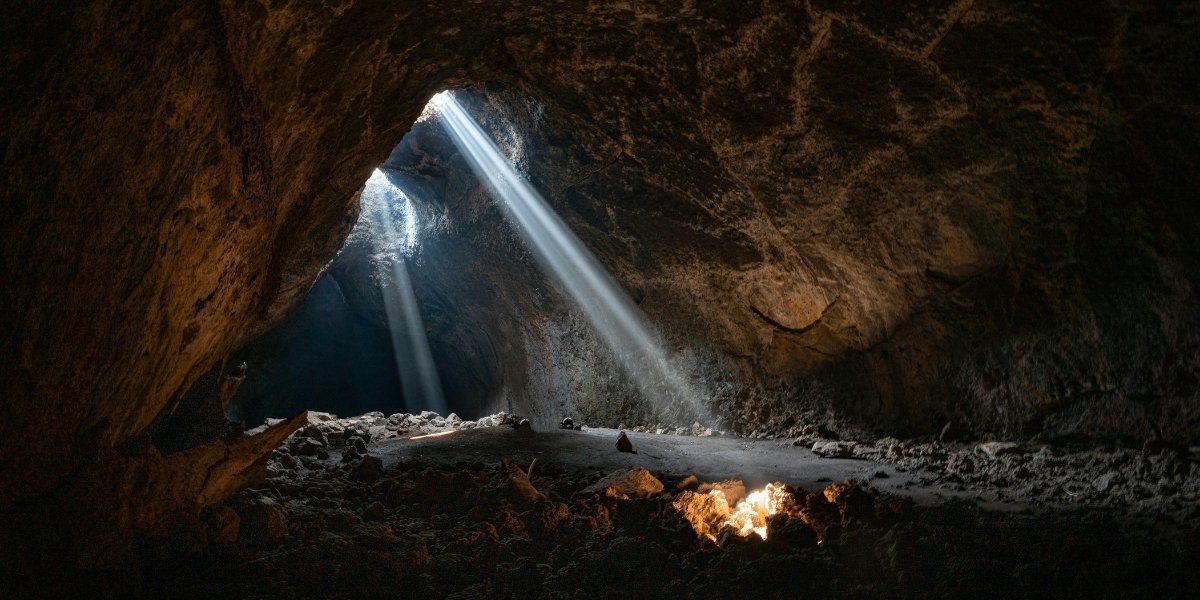
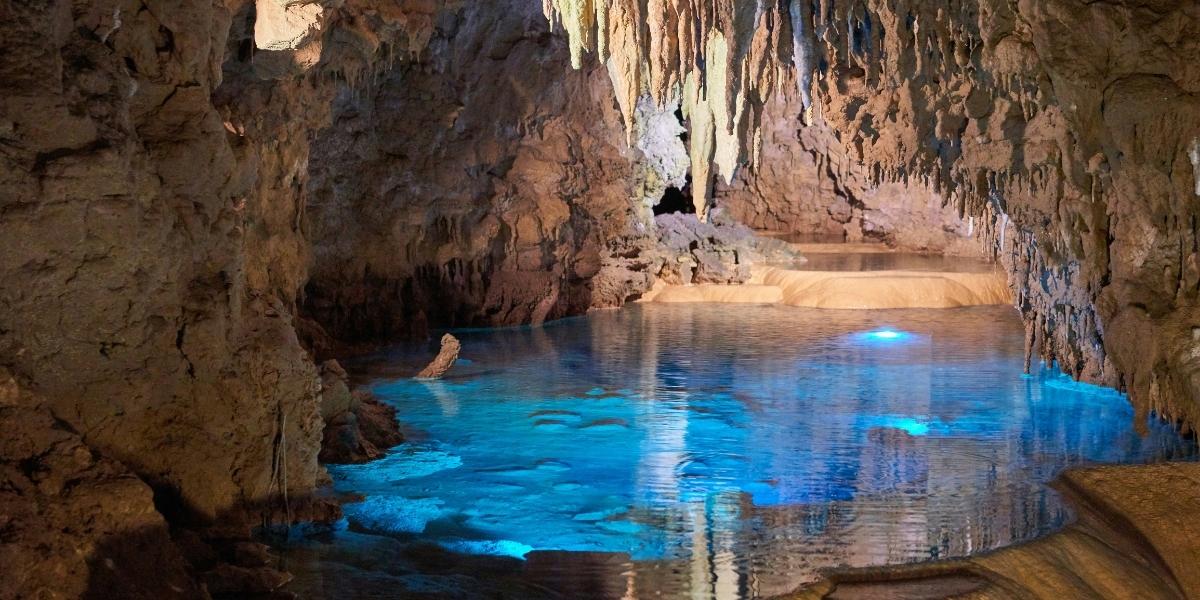
Beneath the familiar landscapes of America lies an astonishing world of natural wonders, sculpted by millennia of geological processes: the extensive network of underground cave systems. These subterranean environments offer a unique glimpse into the Earth’s hidden beauty, characterized by dramatic formations, vast chambers, and serene darkness. From the towering stalagmites to the delicate flowstones, each cave tells a story of water, rock, and time, inviting exploration and sparking a sense of profound wonder. This hidden dimension of the country’s natural heritage offers a distinct type of adventure and discovery for those willing to venture below the surface.
Exploring a cave is an experience unlike any other, offering a profound sense of tranquility and an intimate connection with ancient geological forces. The air inside a cave is often cool and still, and the absence of sunlight creates an environment where unique ecosystems flourish. Visitors can witness breathtaking formations that have grown incrementally over thousands, or even millions, of years, each drip of mineral-rich water contributing to their majestic size. This journey into the earth’s interior provides not only visual splendor but also an educational insight into the slow, powerful forces that shape our planet.
Read Also: Nevada Trails: Adventure Awaits
The United States is home to an incredible diversity of cave systems, ranging from vast national parks dedicated to these underground marvels to smaller, privately managed caverns. Each cave possesses its own distinct characteristics, from the grand scale of some to the intricate details of others, ensuring that no two underground expeditions are exactly alike. These natural formations are not just geological curiosities; they are significant natural resources that inspire awe, provide habitats for unique life forms, and offer unparalleled opportunities for scientific study and adventurous exploration.
How Do Caves Form and What Types Exist?
Caves are formed through a variety of geological processes, with the most common type being solutional caves, also known as karst caves. These form in soluble rocks such as limestone, marble, or dolomite, where groundwater, made slightly acidic by absorbing carbon dioxide from the soil and atmosphere, slowly dissolves the rock over vast periods. This creates intricate networks of fissures, passages, and vast chambers that expand as more rock is dissolved and carried away by underground streams. The continuous flow of water is the primary sculptor, gradually carving out the elaborate subterranean architecture we see today in many famous cave systems.
Beyond solutional caves, other types of cave formations are shaped by different geological forces. Lava tubes, for example, are created during volcanic eruptions when molten lava flows beneath a hardened crust. As the eruption ceases and the molten rock drains away, a hollow tube is left behind, forming a type of cave. Sea caves, on the other hand, are carved out by the relentless erosive power of ocean waves against coastal cliffs, often found along shorelines with softer rock types. Each formation mechanism results in a unique cave morphology, influencing its size, shape, and internal features, making every type a distinct natural wonder.

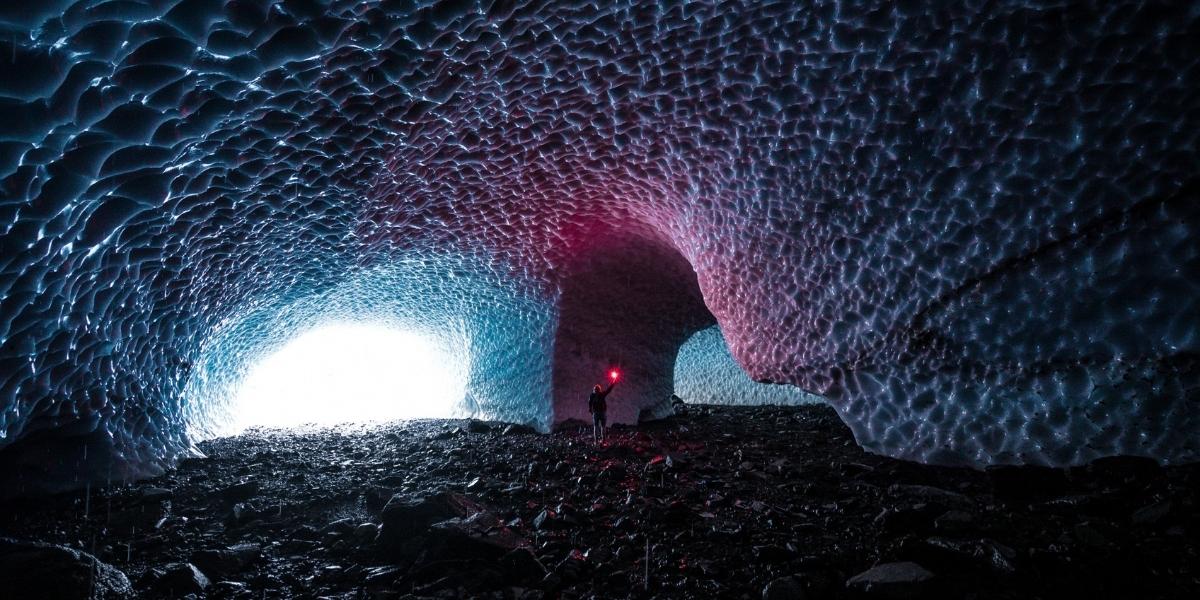
Another fascinating category includes glacier caves, which are formed within ice fields or glaciers by meltwater or geothermal heat, and tectonic caves, created by the movement of Earth’s crust, causing rock fractures and collapses. Regardless of their origin, caves represent a dynamic interplay between geological forces and environmental conditions. The constant, albeit slow, action of water, ice, or tectonic shifts continually sculpts and re-shapes these underground environments. Understanding these formation processes enhances our appreciation for the immense time scales and powerful natural phenomena involved in creating such spectacular subterranean landscapes.
Which Famous Cave Systems Are Found in the US?
The United States boasts an extraordinary array of famous cave systems, each renowned for its unique geological features and vastness. Perhaps the most celebrated is Mammoth Cave National Park in Kentucky, which holds the record as the longest known cave system in the world. Its intricate labyrinth of passages spans hundreds of miles, revealing immense chambers, towering domes, and delicate gypsum flowers. Exploring this vast underground wilderness provides a profound sense of scale and offers a glimpse into millions of years of geological history, drawing visitors from across the globe to witness its unparalleled grandeur.
In New Mexico, Carlsbad Caverns National Park offers another awe-inspiring underground experience. This monumental cave system is famous for its colossal chambers, most notably the “Big Room,” one of the largest single cave chambers in North America. Visitors are captivated by its immense stalagmites, stalactites, and other speleothems, which create an otherworldly landscape. The cave also hosts a spectacular nightly bat flight, adding another layer of natural wonder to the experience. The sheer size and intricate beauty of Carlsbad Caverns highlight the diverse geological artistry found within the Earth’s crust.
Beyond these giants, numerous other notable caves dot the American landscape. Luray Caverns in Virginia, for instance, is celebrated for its stunning formations, including the “Great Stalacpipe Organ,” which produces musical tones by tapping stalactites. Wind Cave National Park in South Dakota is known for its rare boxwork formations and extensive passages, while Jewel Cave National Monument, also in South Dakota, boasts incredibly intricate calcite crystals. Each of these cave systems provides a distinct and memorable experience, showcasing the incredible variety and beauty of America’s underground wonders, inviting continuous exploration and scientific discovery.
What Unique Life Forms Thrive Within a Cave Ecosystem?
The perpetual darkness, stable temperatures, and constant humidity inside a cave create a specialized environment that supports unique and often bizarre life forms adapted to these extreme conditions. Organisms that live permanently underground are known as troglobites, and they exhibit remarkable evolutionary adaptations to survive without light. Many troglobites, such as certain species of fish, salamanders, and insects, have lost their eyesight, relying instead on highly developed senses of touch, smell, and hearing to navigate and find food in absolute darkness. Their colorless, often translucent bodies are another common adaptation to their light-deprived habitat.

The food chain within a cave ecosystem is vastly different from surface environments, as there is no sunlight to support photosynthesis. Instead, troglobites rely on nutrients brought in from the surface, such as decaying plant matter, bat guano, or microscopic organisms carried by water. This scarcity of resources leads to slower metabolisms and longer lifespans for many cave-dwelling creatures, as they conserve energy in their resource-limited habitat. Some specialized bacteria also play a role, deriving energy from inorganic chemical reactions, forming the base of unique chemosynthetic food webs in certain deep cave environments.
Exploring a cave provides a rare opportunity to observe these fascinating creatures that have evolved in isolation for millennia. From blind cave fish in Kentucky to specialized spiders in New Mexico and unique crustaceans in Florida, each cave system can harbor its own distinct array of endemic species. These organisms are highly vulnerable to changes in their environment, making cave conservation vitally important. Their existence underscores the incredible adaptability of life and highlights the hidden biodiversity that thrives beneath our feet, making every discovery within a cave a significant scientific finding.
What Safety Considerations Are Important for Cave Exploration?
Exploring a cave, while captivating, requires strict adherence to safety protocols to ensure a secure and enjoyable experience. For recreational visitors, joining a guided tour is highly recommended, especially in popular commercial caves. These tours are led by experienced guides who know the specific cave system well, can navigate its passages safely, and are trained to handle emergencies. They also provide valuable information about the cave’s geology and history, enriching the overall experience while maintaining a controlled and safe environment for all participants. Never attempt to explore an undeveloped cave without proper training and equipment.
Read Also: The Enduring Quest for Yamashita’s Gold: Myth and Reality
Proper equipment is paramount for any cave exploration. Essential gear includes sturdy closed-toe shoes with good grip, as cave floors can be uneven, slippery, or wet. Headlamps or flashlights are absolutely critical, as caves are entirely dark without artificial light; it is always wise to carry at least three independent light sources for redundancy. Depending on the specific cave and activity, additional gear like helmets to protect against minor bumps, knee pads, and gloves might also be necessary. Dress in layers, as cave temperatures are consistently cool, regardless of the outside weather, ensuring comfort during extended periods underground.
Responsible cave etiquette is vital for both personal safety and the preservation of the delicate cave environment. Always stay on marked trails and follow all instructions from guides. Avoid touching cave formations, as the oils from hands can halt their growth or damage their surfaces. Never disturb wildlife, and carry out everything you carry in, including all trash, to leave no trace of your visit. These practices not only ensure a safe experience for visitors but also help protect these fragile underground ecosystems for future generations to explore and appreciate.